Tannin is the skeleton of red wine (white skeleton is acidity). It gives red wine the structure, complexity and aging ability. Red wine without tannin or insufficient tannin is like a mess of loose sand instead of a solid and beautiful house.

So what are the ingredients of tannin? How does it affect the taste of red wine? Why does it sometimes give a grainy texture in the mouth? And look at the answers below for you.
1.What are the ingredients of tannin?
From the perspective of chemical substances, tannins are polyphenols that can bind and precipitate proteins. The tannins of wine mainly come from grape skins, seeds and stems. Wines aged in oak barrels can also extract certain tannin from oak.

In fact, specifically, wine tannins can be divided into two categories: one is hydrolyzable tannins (soluble in water), which comes from wood (oak), is small in wine and has little effect; Tannins (Condensed Tannins), it comes from the skin and seeds of wine grapes. Condensed tannin in wine is not ordinary grape tannin. It is produced by the polymerization of polyphenols and catechins during the winemaking process, and the tannin polymer in the wine is constantly interrupted. Links are constantly being reorganized. This is a very complicated chemical reaction process, and wine tannins are more complicated than grape tannins.
However, because the tannins in wine mainly come from wine grapes, the amount of tannin in wine is directly linked to the grape variety. Moreover, the quality of grapes will also affect the quality of wine tannins. If the grapes are ripe, the tannins in the wine will be softer and juicy; if the grapes are not ripe, the tannins in the wine will be rougher and bitter.
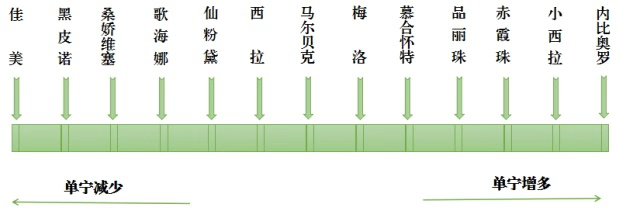
2.How tannins affect the taste of wine?
At the sensory level, tannins have both taste and mouth feel. Its taste is bitter-a pleasant bitter, like the bitterness of espresso or dark chocolate. The bitterness of tannins is mainly caused by catechins and small tannins.

In addition, macromolecular tannins can make the oral mucosa feel wrinkled, which is all our sense of convergence or dryness. Because tannin is a kind of polyphenols, and polyphenols are composed of benzene ring and other substances, they are very active and easily adhere to other substances, so tannins can be linked to multiple proteins at the same time. And saliva contains protein, it is conceivable that when drinking alcohol, tannin will bind with salivary protein and precipitate, so that saliva loses its lubricating effect, and the oral epithelial tissue shrinks, we will feel that the mouth is particularly dry.

Theoretically, tannins are just a kind of molecule, not solid particles, but why do we sometimes feel the granular texture of tannins? Tannin can make the mouth dry and the epithelial tissues in the mouth rub against each other. Without the lubricating effect of saliva, tannins are linked to other substances in the mouth, recombined, and then linked, and their composition becomes more complicated. The current scientific view is that tannins become larger in the oral cavity and slide more easily on the surface of the oral cavity. As for what ingredients make it easier to glide on the surface of the mouth, there is no exact statement.
However, as the wine ages, the tannins will change from dry and rough to smooth and delicate. This is mainly because tannins will gradually combine with acids, pigments and other substances in the liquor to form precipitates. These precipitates will not bring a dry or astringent feeling, and there will be no bitterness.
3.How to determine the amount of tannin in wine?
From the bitterness in the wine, the firmness of the structure, and the fullness of the texture, we can judge the amount of tannin in the wine. When there is a lot of tannin in the wine, the feeling in the back of the mouth, cheeks and gums will be very obvious. Moreover, tannin can be used as Hard, Bitter, Green, Ripe, Coarse, Grainy, or Wood. (wood , It's obvious tannin), soft and so on. To train our perception of tannins, compare high-tannin wines (such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Nebbiolo, Shiraz) with low-tannin wines (such as Camry, Pinot Noir) The different feelings brought by tannins are clear at a glance.

It is also important to note that other ingredients of wine can also affect our perception of tannins in wine. Alcohol will strengthen the bitter taste of tannins and weaken the sense of convergence of tannins, so the higher the alcohol content, the more obvious the bitterness of tannins, otherwise the stronger the sense of convergence. Increased sweetness tends to mask the bitterness of tannins. And acidity ... So the question is, tannin makes saliva less, but acidic substances can stimulate saliva secretion, won't the two conflict with each other? When you can't distinguish between the two, it is wise to carefully observe the reaction of the mouth after swallowing the liquor, and see if the acid is more irritating or the tannin is more convergent.